Top 10 Gate Valves for Optimal Performance in Industrial Applications
In industrial applications, gate valves play a crucial role in regulating fluid flow. These valves offer durability and reliability, making them a popular choice among engineers. Designed to provide minimal flow resistance, gate valves can handle high-pressure environments with ease.
However, not all gate valves are created equal. Some may have limitations in performance, leading to unexpected maintenance costs. Selecting the right gate valve involves considering materials, design, and specific application needs. Users often overlook these details, resulting in suboptimal performance.
This article explores the top 10 gate valves for optimal performance. By focusing on key features and real-world applications, we aim to guide industry professionals in making informed decisions. Understanding each valve's advantages and disadvantages can ultimately lead to improved operational efficiency.

Top 10 Gate Valves: Key Features and Specifications for Industrial Use

When selecting gate valves for industrial applications, key features are crucial. These valves should ensure tight sealing. Look for materials that resist corrosion. Stainless steel and ductile iron are common choices. Valve sizing is vital, as a poor fit can cause leaks.
Flow capacity matters as well. A well-designed valve reduces pressure drop. Ease of maintenance is another important aspect. Valves that permit disassembly make repairs quicker. Some designs even allow for in-line service, saving downtime.
Consider temperature and pressure ratings. Not all valves handle extreme conditions. Carefully assessing these specifications can prevent failures. Sometimes, opting for a lower-rated valve can be tempting. However, this decision can lead to costly damages down the line.
Understanding the Role of Gate Valves in Fluid Control Systems
Gate valves play a critical role in fluid control systems across various industries. They function by either fully opening or closing the flow of liquid or gas. This on-off control provides a straightforward approach to managing fluid dynamics. When properly selected and maintained, gate valves can enhance system efficiency and reliability.
Tips: Always assess the material compatibility of the valve with the fluid. This will prevent accidental leaks or corrosion.
In many cases, gate valves are preferred for their minimal pressure drop. However, they are not ideal for regulating flow. Misapplication can lead to wear and tear, causing costly downtime. Regular inspections are necessary to catch any signs of failure early.
Tips: Implement a routine maintenance schedule. This helps identify issues before they escalate.
Choosing the right gate valve for your system requires careful consideration. Factors such as temperature, pressure, and medium type are crucial. A mismatch can result in suboptimal performance. Always seek expert guidance when in doubt.
Top 10 Gate Valves for Optimal Performance in Industrial Applications
This chart illustrates the performance metrics of the top 10 gate valves focused on various criteria important for fluid control systems. The metrics include Flow Rate (GPM), Pressure Drop (psi), Material Durability, Cost Efficiency, and Maintenance Ease. These parameters help evaluate the efficiency and suitability of gate valves in industrial applications.
Performance Metrics: Flow Coefficient and Pressure Drop in Gate Valves
When selecting gate valves for industrial applications, flow coefficient and pressure drop are critical metrics. The flow coefficient (Cv) measures a valve's ability to pass fluid. In various reports, Cv values for gate valves typically fluctuate between 100 to 1000. A higher Cv indicates better flow capabilities. If the Cv is too low for a specific application, it may cause inefficiencies and increased operational costs.
Pressure drop is another vital aspect. It's essential to monitor how the flow rate affects the pressures on either side of the gate valve. According to industry standards, a pressure drop of 5 to 10% is acceptable. However, exceeding this range can lead to system complications. Accurate calculations must be made to avoid significant energy losses or performance issues.
Design choices also impact these metrics. For instance, the size and material of the valve play a role in flow dynamics. A well-designed gate valve minimizes turbulence and enhances flow efficiency. However, some designs may overlook these factors, leading to potential reflection points in performance. Not all gate valves perform equally under various conditions. Evaluation and testing can sometimes yield unexpected results.
Material Selection: Best Practices for Corrosion Resistance in Valves
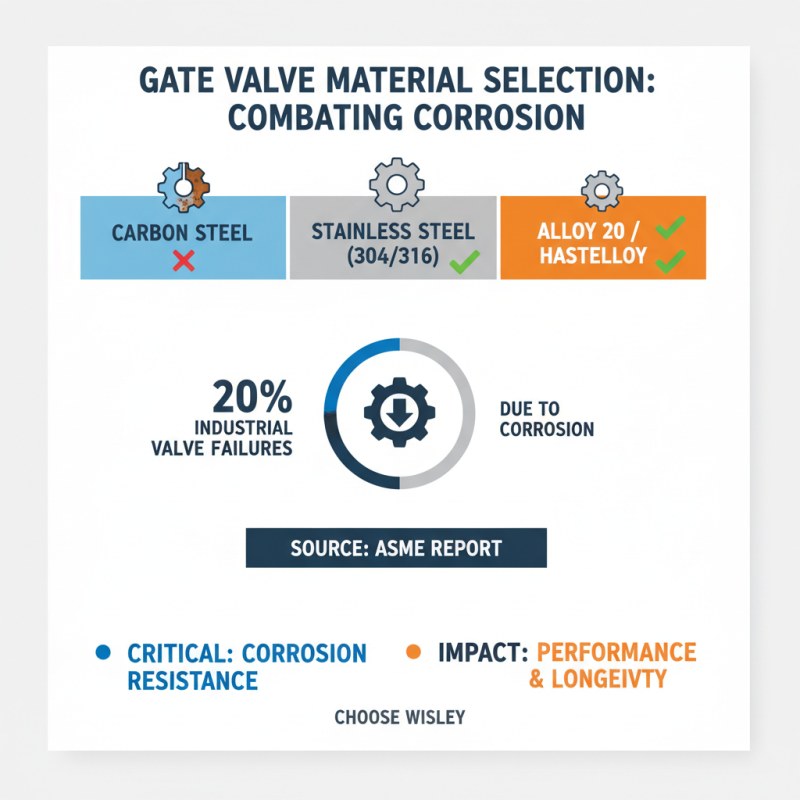
In industrial applications, the selection of materials for gate valves significantly impacts performance and longevity. Corrosion resistance is a critical consideration. According to a report by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, nearly 20% of all industrial valve failures are due to corrosion. This statistic highlights the need for careful material selection.
Stainless steel is often favored for its resistance to oxidation and rust. However, in highly corrosive environments, materials like duplex stainless steel or superalloys may be more suitable. A recent survey indicated that valves made from these advanced materials can reduce maintenance costs by up to 30%. While these materials may carry a higher initial cost, they often yield long-term savings.
Nevertheless, some industries overlook the importance of proper coating and galvanization. An analysis found that improperly coated valves faced a failure rate of over 35%, leading to unscheduled downtime. It's crucial to regularly assess the condition of the materials used. Ignoring corrosion risks can lead to operational inefficiencies. Ultimately, a proactive approach in material selection and maintenance can significantly enhance the lifespan and effectiveness of gate valves in industrial settings.
Maintenance Best Practices for Ensuring Longevity of Gate Valves
Gate valves are essential in industrial applications, controlling fluid flow efficiently. Proper maintenance is vital for their longevity. A well-maintained valve can reduce unexpected downtime and repair costs. Regular inspections should focus on signs of wear, corrosion, or leaks. If you notice rust building up, it might be time for a closer evaluation.
Greasing the valve stem is crucial. A little grease can prevent sticking and ensure smooth operation. However, over-greasing can attract dirt and grime. Be mindful of the balance. Cleaning the valve regularly also helps. Use a soft cloth and mild detergent to remove any surface debris. Skipping this step may lead to bigger problems down the line.
Temperature fluctuations can impact performance. Maintaining consistent temperatures can help avoid expansion and contraction issues. Additionally, training staff on the correct operation can make a significant difference. Sometimes, valves are operated incorrectly, leading to premature wear. Regular training sessions could help in mitigating this risk.
Top 10 Gate Valves for Optimal Performance in Industrial Applications - Maintenance Best Practices for Ensuring Longevity of Gate Valves
| Valve Type | Size (inches) | Material | Pressure Rating (psi) | Temperature Range (°F) | Maintenance Tip |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wedge Gate Valve | 2 | Carbon Steel | 150 | -20 to 250 | Regular inspection for leaks |
| Parallel Slide Gate Valve | 4 | Stainless Steel | 300 | 0 to 400 | Lubricate sliding surfaces regularly |
| Knife Gate Valve | 6 | Cast Iron | 150 | -20 to 300 | Check for blade wear and adjust |
| Hollow Conical Gate Valve | 10 | Bronze | 400 | -10 to 350 | Inspect sealing surfaces often |
| Slab Gate Valve | 8 | PVC | 150 | -10 to 140 | Clean the valve seat regularly |
| Expanding Gate Valve | 12 | Alloy Steel | 600 | -20 to 450 | Ensure proper valve actuation |
| Grooved Gate Valve | 14 | Ductile Iron | 250 | -20 to 300 | Check for corrosion on grooved ends |
| Rising Stem Gate Valve | 16 | Nickel Alloy | 300 | -40 to 400 | Lubricate the stem threads periodically |
| Non-Rising Stem Gate Valve | 20 | Teflon Coated Steel | 150 | -20 to 300 | Adjust packing as needed for leaks |
| Electric Actuated Gate Valve | 24 | Stainless Steel | 600 | -10 to 500 | Inspect electrical components regularly |
Related Posts
-
Top 10 Gate Valves Types and Their Best Applications for Your Projects
-

2026 Best Valve Products for Efficiency and Performance Review?
-

Top 5 Home Valve Solutions to Improve Your Plumbing Efficiency
-

Top 10 Important Facts About Natural Gas Shut Off Valve You Need to Know
-

What is the Function of Saunders Valves in Fluid Control Systems?
-

How to Choose the Right Saunders Valves for Your Applications
